之前有一篇搭建 openvpn 的文章,很久以前写的了,easy-rsa 版本是 2 的吧,这里一篇 3.0.6 的教程奉上,之前的教程链接如下:https://iicats.com/181/
2,0 的配置过程有什么问题,我忘记了,可能回答不上来,这个 3.0.6 的近期给公司搭建了,很多人在用,没什么问题;各位搭建中遇到什么问题直接留言吧,或者邮件也可以~
安装阶段
添加源
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.backup mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo.backup wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
安装 openvpn、easy-rsa(easy-rsa 版本为 3.0.6 为例)
yum install -y openvpn easy-rsa
配置阶段
配置 easy-rsa3.0
cp -r /usr/share/easy-rsa/ /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/
cd 3.0.6/
find / -type f -name "vars.example" | xargs -i cp {} . && mv vars.example vars
这里说明一下,正常来说
easy-rsa-3.0.6安装完之后,vars.example文件在/usr/share/doc/easy-rsa-3.0.6/目录,至于有些人说找不到这个文件,我暂时还没遇到过,可能你的安装方式和我不一致,或版本不同
创建一个新的 PKI 和 CA
$ pwd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6 --- $ ./easyrsa init-pki # 创建空的 pki Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars init-pki complete; you may now create a CA or requests. Your newly created PKI dir is: /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki --- $ ./easyrsa build-ca nopass #创建新的 CA,不使用密码 Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ......................+++ ................................................+++ writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/ca.key.pClvaQ1GLD' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Common Name (eg: your user, host, or server name) [Easy-RSA CA]: 回车 CA creation complete and you may now import and sign cert requests. Your new CA certificate file for publishing is at: /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/ca.crt
创建服务端证书
$ pwd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6 --- $ ./easyrsa gen-req server nopass Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ...........................+++ ..............................................................................+++ writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/server.key.wy7Q0fuG6A' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Common Name (eg: your user, host, or server name) [server]: 回车 Keypair and certificate request completed. Your files are: req: /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/reqs/server.req key: /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/server.key
签约服务端证书
$ pwd
/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6
---
$ ./easyrsa sign server server
Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars
You are about to sign the following certificate.
Please check over the details shown below for accuracy. Note that this request
has not been cryptographically verified. Please be sure it came from a trusted
source or that you have verified the request checksum with the sender.
Request subject, to be signed as a server certificate for 3650 days:
subject=
commonName = server
Type the word 'yes' to continue, or any other input to abort.
Confirm request details: yes
Using configuration from ./openssl-1.0.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
commonName :ASN.1 12:'server'
Certificate is to be certified until Apr 7 14:54:08 2028 GMT (3650 days)
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
Certificate created at: /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/server.crt
创建 Diffie-Hellman
$ pwd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6 --- $ ./easyrsa gen-dh ............................................................ DH parameters of size 2048 created at /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/dh.pem
创建客户端证书
- 复制文件
$ cp -r /usr/share/easy-rsa/ /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa
$ cd /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/
$ cd 3.0.6/
$ find / -type f -name "vars.example" | xargs -i cp {} . && mv vars.example vars
- 生成证书
$ pwd /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/3.0.6 --- $ ./easyrsa init-pki #创建新的 pki Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars init-pki complete; you may now create a CA or requests. Your newly created PKI dir is: /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki --- $ ./easyrsa gen-req eicas nopass #客户证书名为 eicas,木有密码 Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ....................................................+++ ............+++ writing new private key to '/etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/eicas.key.FkrLzXH9Bm' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Common Name (eg: your user, host, or server name) [eicas]: 回车 Keypair and certificate request completed. Your files are: req: /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/3.0.3/pki/reqs/eicas.req key: /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/3.0.3/pki/private/eicas.key
- 最后签约客户端证书
$ cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/
$ pwd
/etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6
---
$ ./easyrsa import-req /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/reqs/eicas.req eicas
Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars
The request has been successfully imported with a short name of: eicas
You may now use this name to perform signing operations on this request.
---
$ ./easyrsa sign client eicas
Note: using Easy-RSA configuration from: ./vars
You are about to sign the following certificate.
Please check over the details shown below for accuracy. Note that this request
has not been cryptographically verified. Please be sure it came from a trusted
source or that you have verified the request checksum with the sender.
Request subject, to be signed as a client certificate for 3650 days:
subject=
commonName = eicas
Type the word 'yes' to continue, or any other input to abort.
Confirm request details: yes
Using configuration from ./openssl-1.0.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows
commonName :ASN.1 12:'eicas'
Certificate is to be certified until Apr 8 01:54:57 2028 GMT (3650 days)
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
Certificate created at: /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/eicas.crt
整理证书
现在所有的证书都已经生成完了,下面来整理一下。
- 服务端所需要的文件
$ mkdir /etc/openvpn/certs $ cd /etc/openvpn/certs/ $ cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/dh.pem . $ cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/ca.crt . $ cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/server.crt . $ cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/server.key . $ ll --- 总用量 20 -rw-------. 1 root root 1172 4 月 11 10:02 ca.crt -rw-------. 1 root root 424 4 月 11 10:03 dh.pem -rw-------. 1 root root 4547 4 月 11 10:03 server.crt -rw-------. 1 root root 1704 4 月 11 10:02 server.key
- 客户端所需的文件
$ mkdir /etc/openvpn/client/eicas/ $ cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/ca.crt /etc/openvpn/client/eicas/ $ cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/issued/eicas.crt /etc/openvpn/client/eicas/ $ cp /etc/openvpn/client/easy-rsa/3.0.6/pki/private/eicas.key /etc/openvpn/client/eicas/ $ ll /etc/openvpn/client/eicas/ --- total 16 -rw------- 1 root root 1147 Feb 11 10:08 ca.crt -rw------- 1 root root 4403 Feb 11 10:08 eicas.crt -rw------- 1 root root 1708 Feb 11 10:09 eicas.key
配置 server.conf
local 0.0.0.0
port 1194 #指定端口
proto tcp #指定协议 (可以指定 udp,udp 比 tcp 快)
dev tun
ca /etc/openvpn/certs/ca.crt
cert /etc/openvpn/certs/server.crt
key /etc/openvpn/certs/server.key
dh /etc/openvpn/certs/dh.pem
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 #给客户端分配的地址池
ifconfig-pool-persist /etc/openvpn/ipp.txt
push "route 192.168.252.0 255.255.0.0" # route 根据实际情况修改
push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" #客户端网关使用 openvpn 服务器网关
push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8" #指定 dns
push "dhcp-option DNS 114.114.114.114"
client-to-client
keepalive 10 120 #心跳检测,10 秒检测一次,2 分钟内没有回应则视为断线
#tls-auth ta.key 0 #服务端值为 0,客户端为 1
cipher AES-256-CBC
comp-lzo
#传输数据压缩
persist-key
persist-tun
status openvpn-status.log
log-append openvpn.log
verb 3
mute 20
开启 IP 转发
$ vim /etc/sysctl.conf # 添加: net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 # 生效 $ sysctl -p
iptables 设置
$ iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 -j MASQUERADE $ iptables-save > /etc/openvpn-rule $ cd /etc/ $ iptables-restore < openvpn-rule
启动 openvpn
$ systemctl start openvpn@server $ systemctl enable openvpn@server
客户端准备
客户端连接工具
Windows:openvpn guiMac:tunnelblick
可能有的涉及到科学上网或者国外网速下载很慢,下面提供我的对象存储下载链接:
Windows 7、8、8.1、server2012:openvpn guiWindows 10:openvpn guiMac:tunnelblick
客户端.ovpn 文件制作
(这里使用把证书内容写入
.ovpn里面,当然在配置文件中写入路径也没问题)
- 客户端所需要的证书路径如下
ll /etc/openvpn/client/eicas/ --- total 16 -rw------- 1 root root 1147 Feb 11 10:08 ca.crt -rw------- 1 root root 4403 Feb 11 10:08 eicas.crt -rw------- 1 root root 1708 Feb 11 10:09 eicas.key
- 本地编辑 client.ovpn
client proto tcp dev tun remote xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 1194 # 服务端公网 IP,默认端口是 1194 # 此处 [inline] 也可以写下载下来本地的客户端各个证书的路径 ca [inline] cert [inline] key [inline] resolv-retry infinite nobind mute-replay-warnings keepalive 20 120 comp-lzo #user openvpn #group openvpn persist-key persist-tun status openvpn-status.log log-append openvpn.log verb 3 mute 20 <ca> ca 证书的内容粘贴此处 </ca> <cert> crt 证书内容粘贴此处 </cert> <key> 秘钥内容粘贴此处 </key>
openvpn gui 使用
- 直接打开软件,导入上述写的
.ovpn文件即可,成功的话,会有提示 mac的那个也是导入就行了,具体还是不会可以百度一下
账号密码设置
开启服务端账号密码登录配置
- 编辑服务端
server.conf文件
$ vim /etc/openvpn/server.conf # 添加如下内容 # use username and password login script-security 3 auth-user-pass-verify /etc/openvpn/checkpsw.sh via-env client-cert-not-required username-as-common-name
- 添加密码检查脚本 checkpsw.sh
$ vim /etc/openvpn/checkpsw.sh
---
#!/bin/sh
###########################################################
#
# This script will authenticate OpenVPN users against
# a plain text file. The passfile should simply contain
# one row per user with the username first followed by
# one or more space(s) or tab(s) and then the password.
PASSFILE="/etc/openvpn/psw-file" # 账号密码的路径
LOG_FILE="/etc/openvpn/openvpn-password.log" # 账号密码的日志
TIME_STAMP=`date "+%Y-%m-%d %T"`
###########################################################
if [ ! -r "${PASSFILE}" ]; then
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: Could not open password file \"${PASSFILE}\" for reading." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
fi
CORRECT_PASSWORD=`awk '!/^;/&&!/^#/&&$1=="'${username}'"{print $2;exit}' ${PASSFILE}`
if [ "${CORRECT_PASSWORD}" = "" ]; then
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: User does not exist: username=\"${username}\", password=\"${password}\"." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
fi
if [ "${password}" = "${CORRECT_PASSWORD}" ]; then
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: Successful authentication: username=\"${username}\"." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 0
fi
echo "${TIME_STAMP}: Incorrect password: username=\"${username}\", password=\"${password}\"." >> ${LOG_FILE}
exit 1
- 添加账号密码
$ vim /etc/openvpn/psw-file # 账号+空格+密码的形式,例如: test 123456
- 重启 openvpn
systemctl restart openvpn@server
设置客户端.ovpn 密码账号登录内容
- 编辑之前创建的
client.ovpn文件,添加一行:
auth-user-pass
- 完整如下
client proto tcp dev tun remote xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 1194 # 服务端公网 IP,默认端口是 1194 # 此处 [inline] 也可以写下载下来本地的客户端各个证书的路径 ca [inline] cert [inline] key [inline] resolv-retry infinite nobind mute-replay-warnings keepalive 20 120 comp-lzo #user openvpn #group openvpn persist-key persist-tun status openvpn-status.log log-append openvpn.log verb 3 auth-user-pass mute 20 <ca> ca 证书的内容粘贴此处 </ca> crt 证书内容粘贴此处 <cert> </cert> <key> 秘钥内容粘贴此处 </key>
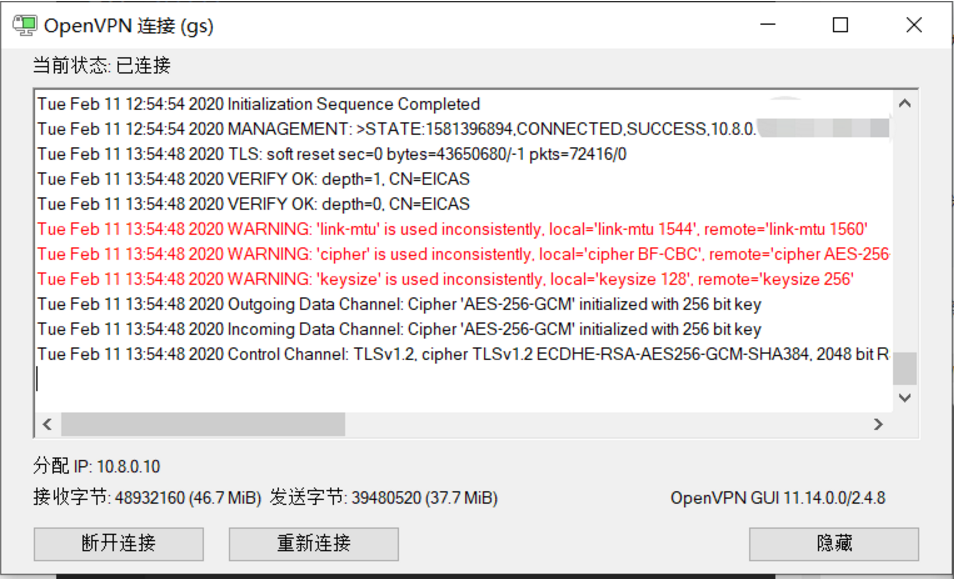
之后重新连接即可
Windows 10 运行成功效果图
自动化安装脚本
- 支持自动化安装、自动化生成客户端配置文件
- 支持新增客户端配置文件
- 支持移除客户端配置文件
- 支持卸载服务端
- 不支持多用户支持 (可自行修改程序实现)
#!/bin/bash
# Detect Debian users running the script with "sh" instead of bash
if readlink /proc/$$/exe | grep -q "dash"; then
echo 'This installer needs to be run with "bash", not "sh".'
exit
fi
# Discard stdin. Needed when running from an one-liner which includes a newline
read -N 999999 -t 0.001
# Detect OpenVZ 6
if [[ $(uname -r | cut -d "." -f 1) -eq 2 ]]; then
echo "The system is running an old kernel, which is incompatible with this installer."
exit
fi
# Detect OS
# $os_version variables aren't always in use, but are kept here for convenience
if grep -qs "ubuntu" /etc/os-release; then
os="ubuntu"
os_version=$(grep 'VERSION_ID' /etc/os-release | cut -d '"' -f 2 | tr -d '.')
group_name="nogroup"
elif [[ -e /etc/debian_version ]]; then
os="debian"
os_version=$(grep -oE '[0-9]+' /etc/debian_version | head -1)
group_name="nogroup"
elif [[ -e /etc/centos-release ]]; then
os="centos"
os_version=$(grep -oE '[0-9]+' /etc/centos-release | head -1)
group_name="nobody"
elif [[ -e /etc/fedora-release ]]; then
os="fedora"
os_version=$(grep -oE '[0-9]+' /etc/fedora-release | head -1)
group_name="nobody"
else
echo "This installer seems to be running on an unsupported distribution.
Supported distributions are Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Fedora."
exit
fi
if [[ "$os" == "ubuntu" && "$os_version" -lt 1804 ]]; then
echo "Ubuntu 18.04 or higher is required to use this installer.
This version of Ubuntu is too old and unsupported."
exit
fi
if [[ "$os" == "debian" && "$os_version" -lt 9 ]]; then
echo "Debian 9 or higher is required to use this installer.
This version of Debian is too old and unsupported."
exit
fi
if [[ "$os" == "centos" && "$os_version" -lt 7 ]]; then
echo "CentOS 7 or higher is required to use this installer.
This version of CentOS is too old and unsupported."
exit
fi
# Detect environments where $PATH does not include the sbin directories
if ! grep -q sbin <<< "$PATH"; then
echo '$PATH does not include sbin. Try using "su -" instead of "su".'
exit
fi
if [[ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]]; then
echo "This installer needs to be run with superuser privileges."
exit
fi
if [[ ! -e /dev/net/tun ]] || ! ( exec 7<>/dev/net/tun ) 2>/dev/null; then
echo "The system does not have the TUN device available.
TUN needs to be enabled before running this installer."
exit
fi
new_client () {
# Generates the custom client.ovpn
{
cat /etc/openvpn/server/client-common.txt
echo "<ca>"
cat /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/ca.crt
echo "</ca>"
echo "<cert>"
sed -ne '/BEGIN CERTIFICATE/,$ p' /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/issued/"$client".crt
echo "</cert>"
echo "<key>"
cat /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/private/"$client".key
echo "</key>"
echo "<tls-crypt>"
sed -ne '/BEGIN OpenVPN Static key/,$ p' /etc/openvpn/server/tc.key
echo "</tls-crypt>"
} > ~/"$client".ovpn
}
if [[ ! -e /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf ]]; then
clear
echo 'Welcome to this OpenVPN road warrior installer!'
# If system has a single IPv4, it is selected automatically. Else, ask the user
if [[ $(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vEc '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}') -eq 1 ]]; then
ip=$(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vE '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}')
else
number_of_ip=$(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vEc '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}')
echo
echo "Which IPv4 address should be used?"
ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vE '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | nl -s ') '
read -p "IPv4 address [1]: " ip_number
until [[ -z "$ip_number" || "$ip_number" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$ip_number" -le "$number_of_ip" ]]; do
echo "$ip_number: invalid selection."
read -p "IPv4 address [1]: " ip_number
done
[[ -z "$ip_number" ]] && ip_number="1"
ip=$(ip -4 addr | grep inet | grep -vE '127(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | sed -n "$ip_number"p)
fi
# If $ip is a private IP address, the server must be behind NAT
if echo "$ip" | grep -qE '^(10\.|172\.1[6789]\.|172\.2[0-9]\.|172\.3[01]\.|192\.168)'; then
echo
echo "This server is behind NAT. What is the public IPv4 address or hostname?"
# Get public IP and sanitize with grep
get_public_ip=$(grep -m 1 -oE '^[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}$' <<< "$(wget -T 10 -t 1 -4qO- "http://ip1.dynupdate.no-ip.com/" || curl -m 10 -4Ls "http://ip1.dynupdate.no-ip.com/")")
read -p "Public IPv4 address / hostname [$get_public_ip]: " public_ip
# If the checkip service is unavailable and user didn't provide input, ask again
until [[ -n "$get_public_ip" || -n "$public_ip" ]]; do
echo "Invalid input."
read -p "Public IPv4 address / hostname: " public_ip
done
[[ -z "$public_ip" ]] && public_ip="$get_public_ip"
fi
# If system has a single IPv6, it is selected automatically
if [[ $(ip -6 addr | grep -c 'inet6 [23]') -eq 1 ]]; then
ip6=$(ip -6 addr | grep 'inet6 [23]' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '([0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}:){1,7}[0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}')
fi
# If system has multiple IPv6, ask the user to select one
if [[ $(ip -6 addr | grep -c 'inet6 [23]') -gt 1 ]]; then
number_of_ip6=$(ip -6 addr | grep -c 'inet6 [23]')
echo
echo "Which IPv6 address should be used?"
ip -6 addr | grep 'inet6 [23]' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '([0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}:){1,7}[0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}' | nl -s ') '
read -p "IPv6 address [1]: " ip6_number
until [[ -z "$ip6_number" || "$ip6_number" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$ip6_number" -le "$number_of_ip6" ]]; do
echo "$ip6_number: invalid selection."
read -p "IPv6 address [1]: " ip6_number
done
[[ -z "$ip6_number" ]] && ip6_number="1"
ip6=$(ip -6 addr | grep 'inet6 [23]' | cut -d '/' -f 1 | grep -oE '([0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}:){1,7}[0-9a-fA-F]{0,4}' | sed -n "$ip6_number"p)
fi
echo
echo "Which protocol should OpenVPN use?"
echo " 1) UDP (recommended)"
echo " 2) TCP"
read -p "Protocol [1]: " protocol
until [[ -z "$protocol" || "$protocol" =~ ^[12]$ ]]; do
echo "$protocol: invalid selection."
read -p "Protocol [1]: " protocol
done
case "$protocol" in
1|"")
protocol=udp
;;
2)
protocol=tcp
;;
esac
echo
echo "What port should OpenVPN listen to?"
read -p "Port [1194]: " port
until [[ -z "$port" || "$port" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$port" -le 65535 ]]; do
echo "$port: invalid port."
read -p "Port [1194]: " port
done
[[ -z "$port" ]] && port="1194"
echo
echo "Select a DNS server for the clients:"
echo " 1) Current system resolvers"
echo " 2) Google"
echo " 3) 1.1.1.1"
echo " 4) OpenDNS"
echo " 5) Quad9"
echo " 6) AdGuard"
read -p "DNS server [1]: " dns
until [[ -z "$dns" || "$dns" =~ ^[1-6]$ ]]; do
echo "$dns: invalid selection."
read -p "DNS server [1]: " dns
done
echo
echo "Enter a name for the first client:"
read -p "Name [client]: " unsanitized_client
# Allow a limited set of characters to avoid conflicts
client=$(sed 's/[^0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_-]/_/g' <<< "$unsanitized_client")
[[ -z "$client" ]] && client="client"
echo
echo "OpenVPN installation is ready to begin."
# Install a firewall in the rare case where one is not already available
if ! systemctl is-active --quiet firewalld.service && ! hash iptables 2>/dev/null; then
if [[ "$os" == "centos" || "$os" == "fedora" ]]; then
firewall="firewalld"
# We don't want to silently enable firewalld, so we give a subtle warning
# If the user continues, firewalld will be installed and enabled during setup
echo "firewalld, which is required to manage routing tables, will also be installed."
elif [[ "$os" == "debian" || "$os" == "ubuntu" ]]; then
# iptables is way less invasive than firewalld so no warning is given
firewall="iptables"
fi
fi
read -n1 -r -p "Press any key to continue..."
# If running inside a container, disable LimitNPROC to prevent conflicts
if systemd-detect-virt -cq; then
mkdir /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-server@server.service.d/ 2>/dev/null
echo "[Service]
LimitNPROC=infinity" > /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-server@server.service.d/disable-limitnproc.conf
fi
if [[ "$os" = "debian" || "$os" = "ubuntu" ]]; then
apt-get update
apt-get install -y openvpn openssl ca-certificates $firewall
elif [[ "$os" = "centos" ]]; then
yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y openvpn openssl ca-certificates tar $firewall
else
# Else, OS must be Fedora
dnf install -y openvpn openssl ca-certificates tar $firewall
fi
# If firewalld was just installed, enable it
if [[ "$firewall" == "firewalld" ]]; then
systemctl enable --now firewalld.service
fi
# Get easy-rsa
easy_rsa_url='https://github.com/OpenVPN/easy-rsa/releases/download/v3.0.8/EasyRSA-3.0.8.tgz'
mkdir -p /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
{ wget -qO- "$easy_rsa_url" 2>/dev/null || curl -sL "$easy_rsa_url" ; } | tar xz -C /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/ --strip-components 1
chown -R root:root /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
cd /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
# Create the PKI, set up the CA and the server and client certificates
./easyrsa init-pki
./easyrsa --batch build-ca nopass
EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE=3650 ./easyrsa build-server-full server nopass
EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE=3650 ./easyrsa build-client-full "$client" nopass
EASYRSA_CRL_DAYS=3650 ./easyrsa gen-crl
# Move the stuff we need
cp pki/ca.crt pki/private/ca.key pki/issued/server.crt pki/private/server.key pki/crl.pem /etc/openvpn/server
# CRL is read with each client connection, while OpenVPN is dropped to nobody
chown nobody:"$group_name" /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
# Without +x in the directory, OpenVPN can't run a stat() on the CRL file
chmod o+x /etc/openvpn/server/
# Generate key for tls-crypt
openvpn --genkey --secret /etc/openvpn/server/tc.key
# Create the DH parameters file using the predefined ffdhe2048 group
echo '-----BEGIN DH PARAMETERS-----
MIIBCAKCAQEA//////////+t+FRYortKmq/cViAnPTzx2LnFg84tNpWp4TZBFGQz
+8yTnc4kmz75fS/jY2MMddj2gbICrsRhetPfHtXV/WVhJDP1H18GbtCFY2VVPe0a
87VXE15/V8k1mE8McODmi3fipona8+/och3xWKE2rec1MKzKT0g6eXq8CrGCsyT7
YdEIqUuyyOP7uWrat2DX9GgdT0Kj3jlN9K5W7edjcrsZCwenyO4KbXCeAvzhzffi
7MA0BM0oNC9hkXL+nOmFg/+OTxIy7vKBg8P+OxtMb61zO7X8vC7CIAXFjvGDfRaD
ssbzSibBsu/6iGtCOGEoXJf//////////wIBAg==
-----END DH PARAMETERS-----' > /etc/openvpn/server/dh.pem
# Generate server.conf
echo "local $ip
port $port
proto $protocol
dev tun
ca ca.crt
cert server.crt
key server.key
dh dh.pem
auth SHA512
tls-crypt tc.key
topology subnet
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0" > /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
# IPv6
if [[ -z "$ip6" ]]; then
echo 'push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
else
echo 'server-ipv6 fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "redirect-gateway def1 ipv6 bypass-dhcp"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
fi
echo 'ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
# DNS
case "$dns" in
1|"")
# Locate the proper resolv.conf
# Needed for systems running systemd-resolved
if grep -q '^nameserver 127.0.0.53' "/etc/resolv.conf"; then
resolv_conf="/run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf"
else
resolv_conf="/etc/resolv.conf"
fi
# Obtain the resolvers from resolv.conf and use them for OpenVPN
grep -v '^#\|^;' "$resolv_conf" | grep '^nameserver' | grep -oE '[0-9]{1,3}(\.[0-9]{1,3}){3}' | while read line; do
echo "push \"dhcp-option DNS $line\"" >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
done
;;
2)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.4.4"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
3)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 1.1.1.1"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 1.0.0.1"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
4)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
5)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 9.9.9.9"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 149.112.112.112"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
6)
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 94.140.14.14"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
echo 'push "dhcp-option DNS 94.140.15.15"' >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
;;
esac
echo "keepalive 10 120
cipher AES-256-CBC
user nobody
group $group_name
persist-key
persist-tun
verb 3
crl-verify crl.pem" >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
if [[ "$protocol" = "udp" ]]; then
echo "explicit-exit-notify" >> /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf
fi
# Enable net.ipv4.ip_forward for the system
echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward=1' > /etc/sysctl.d/30-openvpn-forward.conf
# Enable without waiting for a reboot or service restart
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
if [[ -n "$ip6" ]]; then
# Enable net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding for the system
echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1" >> /etc/sysctl.d/30-openvpn-forward.conf
# Enable without waiting for a reboot or service restart
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/forwarding
fi
if systemctl is-active --quiet firewalld.service; then
# Using both permanent and not permanent rules to avoid a firewalld
# reload.
# We don't use --add-service=openvpn because that would only work with
# the default port and protocol.
firewall-cmd --add-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --add-source=10.8.0.0/24
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-source=10.8.0.0/24
# Set NAT for the VPN subnet
firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
if [[ -n "$ip6" ]]; then
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --add-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
fi
else
# Create a service to set up persistent iptables rules
iptables_path=$(command -v iptables)
ip6tables_path=$(command -v ip6tables)
# nf_tables is not available as standard in OVZ kernels. So use iptables-legacy
# if we are in OVZ, with a nf_tables backend and iptables-legacy is available.
if [[ $(systemd-detect-virt) == "openvz" ]] && readlink -f "$(command -v iptables)" | grep -q "nft" && hash iptables-legacy 2>/dev/null; then
iptables_path=$(command -v iptables-legacy)
ip6tables_path=$(command -v ip6tables-legacy)
fi
echo "[Unit]
Before=network.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=$iptables_path -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to $ip
ExecStart=$iptables_path -I INPUT -p $protocol --dport $port -j ACCEPT
ExecStart=$iptables_path -I FORWARD -s 10.8.0.0/24 -j ACCEPT
ExecStart=$iptables_path -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$iptables_path -t nat -D POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to $ip
ExecStop=$iptables_path -D INPUT -p $protocol --dport $port -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$iptables_path -D FORWARD -s 10.8.0.0/24 -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$iptables_path -D FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT" > /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
if [[ -n "$ip6" ]]; then
echo "ExecStart=$ip6tables_path -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to $ip6
ExecStart=$ip6tables_path -I FORWARD -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j ACCEPT
ExecStart=$ip6tables_path -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$ip6tables_path -t nat -D POSTROUTING -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to $ip6
ExecStop=$ip6tables_path -D FORWARD -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j ACCEPT
ExecStop=$ip6tables_path -D FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT" >> /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
fi
echo "RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target" >> /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
systemctl enable --now openvpn-iptables.service
fi
# If SELinux is enabled and a custom port was selected, we need this
if sestatus 2>/dev/null | grep "Current mode" | grep -q "enforcing" && [[ "$port" != 1194 ]]; then
# Install semanage if not already present
if ! hash semanage 2>/dev/null; then
if [[ "$os_version" -eq 7 ]]; then
# Centos 7
yum install -y policycoreutils-python
else
# CentOS 8 or Fedora
dnf install -y policycoreutils-python-utils
fi
fi
semanage port -a -t openvpn_port_t -p "$protocol" "$port"
fi
# If the server is behind NAT, use the correct IP address
[[ -n "$public_ip" ]] && ip="$public_ip"
# client-common.txt is created so we have a template to add further users later
echo "client
dev tun
proto $protocol
remote $ip $port
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
remote-cert-tls server
auth SHA512
cipher AES-256-CBC
ignore-unknown-option block-outside-dns
block-outside-dns
verb 3" > /etc/openvpn/server/client-common.txt
# Enable and start the OpenVPN service
systemctl enable --now openvpn-server@server.service
# Generates the custom client.ovpn
new_client
echo
echo "Finished!"
echo
echo "The client configuration is available in:" ~/"$client.ovpn"
echo "New clients can be added by running this script again."
else
clear
echo "OpenVPN is already installed."
echo
echo "Select an option:"
echo " 1) Add a new client"
echo " 2) Revoke an existing client"
echo " 3) Remove OpenVPN"
echo " 4) Exit"
read -p "Option: " option
until [[ "$option" =~ ^[1-4]$ ]]; do
echo "$option: invalid selection."
read -p "Option: " option
done
case "$option" in
1)
echo
echo "Provide a name for the client:"
read -p "Name: " unsanitized_client
client=$(sed 's/[^0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_-]/_/g' <<< "$unsanitized_client")
while [[ -z "$client" || -e /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/issued/"$client".crt ]]; do
echo "$client: invalid name."
read -p "Name: " unsanitized_client
client=$(sed 's/[^0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_-]/_/g' <<< "$unsanitized_client")
done
cd /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE=3650 ./easyrsa build-client-full "$client" nopass
# Generates the custom client.ovpn
new_client
echo
echo "$client added. Configuration available in:" ~/"$client.ovpn"
exit
;;
2)
# This option could be documented a bit better and maybe even be simplified
# ...but what can I say, I want some sleep too
number_of_clients=$(tail -n +2 /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/index.txt | grep -c "^V")
if [[ "$number_of_clients" = 0 ]]; then
echo
echo "There are no existing clients!"
exit
fi
echo
echo "Select the client to revoke:"
tail -n +2 /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/index.txt | grep "^V" | cut -d '=' -f 2 | nl -s ') '
read -p "Client: " client_number
until [[ "$client_number" =~ ^[0-9]+$ && "$client_number" -le "$number_of_clients" ]]; do
echo "$client_number: invalid selection."
read -p "Client: " client_number
done
client=$(tail -n +2 /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/index.txt | grep "^V" | cut -d '=' -f 2 | sed -n "$client_number"p)
echo
read -p "Confirm $client revocation? [y/N]: " revoke
until [[ "$revoke" =~ ^[yYnN]*$ ]]; do
echo "$revoke: invalid selection."
read -p "Confirm $client revocation? [y/N]: " revoke
done
if [[ "$revoke" =~ ^[yY]$ ]]; then
cd /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/
./easyrsa --batch revoke "$client"
EASYRSA_CRL_DAYS=3650 ./easyrsa gen-crl
rm -f /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
cp /etc/openvpn/server/easy-rsa/pki/crl.pem /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
# CRL is read with each client connection, when OpenVPN is dropped to nobody
chown nobody:"$group_name" /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem
echo
echo "$client revoked!"
else
echo
echo "$client revocation aborted!"
fi
exit
;;
3)
echo
read -p "Confirm OpenVPN removal? [y/N]: " remove
until [[ "$remove" =~ ^[yYnN]*$ ]]; do
echo "$remove: invalid selection."
read -p "Confirm OpenVPN removal? [y/N]: " remove
done
if [[ "$remove" =~ ^[yY]$ ]]; then
port=$(grep '^port ' /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf | cut -d " " -f 2)
protocol=$(grep '^proto ' /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf | cut -d " " -f 2)
if systemctl is-active --quiet firewalld.service; then
ip=$(firewall-cmd --direct --get-rules ipv4 nat POSTROUTING | grep '\-s 10.8.0.0/24 '"'"'!'"'"' -d 10.8.0.0/24' | grep -oE '[^ ]+$')
# Using both permanent and not permanent rules to avoid a firewalld reload.
firewall-cmd --remove-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --remove-source=10.8.0.0/24
firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port="$port"/"$protocol"
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --remove-source=10.8.0.0/24
firewall-cmd --direct --remove-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --remove-rule ipv4 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s 10.8.0.0/24 ! -d 10.8.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to "$ip"
if grep -qs "server-ipv6" /etc/openvpn/server/server.conf; then
ip6=$(firewall-cmd --direct --get-rules ipv6 nat POSTROUTING | grep '\-s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 '"'"'!'"'"' -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64' | grep -oE '[^ ]+$')
firewall-cmd --zone=trusted --remove-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --remove-source=fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64
firewall-cmd --direct --remove-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --remove-rule ipv6 nat POSTROUTING 0 -s fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 ! -d fddd:1194:1194:1194::/64 -j SNAT --to "$ip6"
fi
else
systemctl disable --now openvpn-iptables.service
rm -f /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-iptables.service
fi
if sestatus 2>/dev/null | grep "Current mode" | grep -q "enforcing" && [[ "$port" != 1194 ]]; then
semanage port -d -t openvpn_port_t -p "$protocol" "$port"
fi
systemctl disable --now openvpn-server@server.service
rm -rf /etc/openvpn/server
rm -f /etc/systemd/system/openvpn-server@server.service.d/disable-limitnproc.conf
rm -f /etc/sysctl.d/30-openvpn-forward.conf
if [[ "$os" = "debian" || "$os" = "ubuntu" ]]; then
apt-get remove --purge -y openvpn
else
# Else, OS must be CentOS or Fedora
yum remove -y openvpn
fi
echo
echo "OpenVPN removed!"
else
echo
echo "OpenVPN removal aborted!"
fi
exit
;;
4)
exit
;;
esac
fi
本文作者为 olei,转载请注明。

一 gi 我里 giao giao,最新版还能 Android 连接吗,好久没玩这个了。
@凌一可以呀,这个只是一个内网 vpn 而已,并非科学上网哦
@olei 不错 加 qq 了 开源精神 不错 好兄弟~
你有没有遇到 tap windows 数字签名的问题啊?因为数字签名不对,导致 tap-windows 无法正常工作。
谢谢大佬
文章不错支持一下
感谢分享 赞一个
支持博主!!!